Sustainability is a megatrend, and all enterprises are striving to increase their sustainability efforts. Sustainability has become a boardroom priority now, and almost all big enterprises are taking net-zero pledges. For manufacturing enterprises, net-zero factories are one of the most important steps towards fulfilling net-zero pledges. Here Industry 4.0 can help in their net-zero factory journey.
Sustainability services can be classified into five categories: energy, material, pollution, water, and food or forest. These categories are further divided based on changes in usage mix, reduction in wastage, or increase in efficiency. (Read here details about sustainability engineering scope).
Out of these five categories, four categories are applicable in factories: energy, material, pollution, and water. Industry 4.0 capabilities help in these four categories, as shown in the below Exhibit.
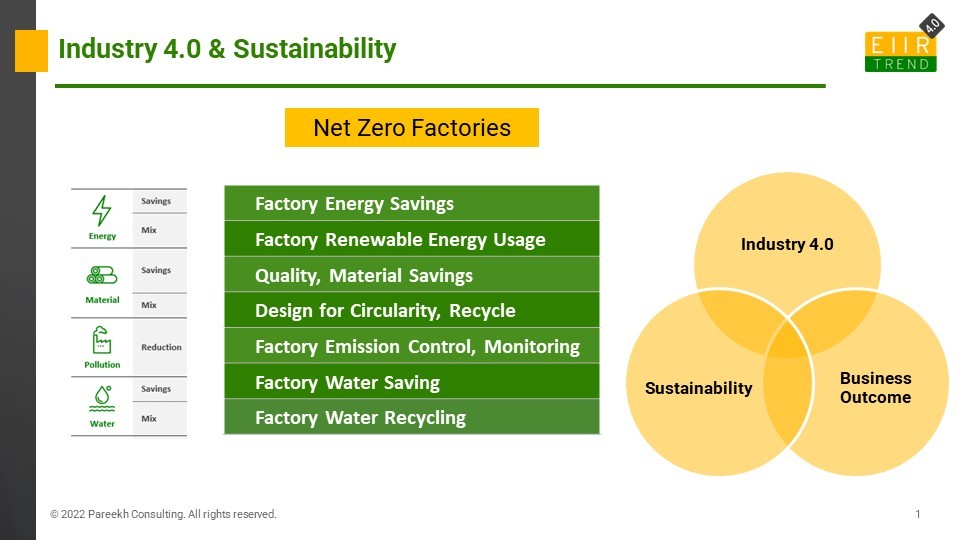
There are seven broad areas across four categories of energy, material, pollution, and water that Industry 4.0 can help.
Factory Energy Savings: Industry 4.0 can help energy savings in three ways.
- Automation and new technology on the shopfloor: These technologies increase capacity and reduce energy requirements per unit. For example, Panasonic, in its net-zero factory in China, established an automatic production line driven by dual-arm robots. This increased the production capacity by 10% with the same amount of energy consumption as before,
- Smart energy management and monitoring solutions: Most Industry 4.0 service providers have smart energy monitoring and management solutions that help identify energy-saving opportunities using monitoring, analytics, and AI. In Panasonic net-zero factory, the application of this solution increased energy savings by 14%
- Energy savings in non-core processes in factories: These processes include material supply, logistics, among others. For example, in parts logistics at Automobili Lamborghini, rail transport of Urus body shells resulted in an 85% reduction in CO₂ emissions compared to road transport. In another example, Spanish carmaker SEAT tests drone deliveries of parts to factory from parts store which saves energy compared to the vehicle deliveries.
Factory Renewable Energy Usage: Changing the energy mix and using more renewable energy. These are applicable both in the direct energy usage in plants as well as in the supply chain.
- Direct Plant: Bridgestone is now using 100% renewable energy to power all its European plants
- Supply Chain: Schaeffler is buying green steel from Swedish start-up company H2greensteel
Material Savings: Industry 4.0 can help material savings in three ways:
- Quality Improvement: Automation, AI, visual analytics in the shopfloor quality monitoring process can help improve quality by detecting problems early and quick rectification. In Panasonic’s net-zero factory, automation contributed to the reduction of the number of defective products and hence material savings
- Yield Improvement: Yield improvement with operational analytics and AI is possible in many factory setups, and it directly contributes to reducing wastage and scrap.
- Generative Design: With Industry 4.0 and AI, it is possible to use generative design with desired functionality and performance but optimized for material savings.
Design for Circularity, Recycle: Industry 4.0 can help in design, reuse, remanufacturing for circularity, and also development and testing of recycled material
- Reuse with Manuufcaturing: Manufacturers are attempting different strategies for reuse using Industry 4.0. Toyota’s UK arm has prepared a proposal to Remanufcature vehicles in their smart factories after their use cycle is completed. Renault to create a ‘Refactory’ in Spain. In order to convert the potential value generated by the circular economy, this will be structured around four areas of activity, from maintenance to recycling, in order to support the entire life of the vehicle: Re-Trofit, Re-Energy, Re-Cycle, Re-Start.
- Design for circularity: With Industry 4.0, products can be designed optimally for circularity and reuse.
- New Materials: With Industry 4.0 and AI, it is possible to develop new material combinations with recycled material. Its most use is in packaging.
Factory Emission Control, Monitoring: Industry 4.0 can help in emission monitoring and control, including carbon capture at plants.
- Emission Control: Emissions can be monitored using Industry 4.0 solutions, and emission reduction strategies can be worked out, including prioritized technology upgrade
- Carbon Capture: DENSO is testing its CO2 circulation plant. The CO2 circulation plant is designed to capture CO2 primarily generated by the plant and recycle it as an energy source for the facility and other uses.
Factory Water Savings: Industry 4.0 can help in reduction in both water wastage and consumption with monitoring, IoT, AI, analytics.
- Reduction in Water: Wastage: High water-consuming industries such as the beverage industry can reduce water wastage with Industry 4,0 technologies.
- Reduction in Water Consumption: Many enterprises aspire to reduce water consumption. For example, Audi plans to cut water consumption in production by half.
Factory Water Recycling: In some factory setups, it is possible to use recycled water for both core and non-core activities
- Recycling Wastewater in core processes: The new Northvolt factory in Torslanda will use recycled wastewater for cooling.
- Recycling Wastewater in non-core processes: For example, in landscaping and other activities.
How to Start: Intersection of Sustainability, Industry 4.0 & Business Outcome in Factories
Industry 4.0 enables a step-change in factory performance leveraging technology. Sustainability is one of the important dimensions of company performance. If a company saves energy with the help of Industry 4.0 technology, it helps in sustainability and also in saving costs. If enterprises start with use cases that are at the intersection of Industry 4.0, Sustainability, and Business Outcome, that will ensure sustainability initiatives are taken as a priority by all stakeholders and create internal momentum to scale them further.
Bottom Line: Industry 4.0 can enable sustainability and net-zero factories while accelerating business performance. Therefore sustainability charter should be aligned with Industry 4.0, and it should give further impetus to Industry 4.0 investments. Enterprise should learn from their Industry 4.0 journey and should not fall into the trap of pilots and PoCs that don’t scale. Here the target is clear, i.e., net-zero factories. The proper planning and execution with the help of partners can help enterprises achieve their net-zero factory targets.








